The 10 Most Recommended Supplements for Improving Concentration and Memory
Improving cognitive function, especially focus, concentration, and memory, is a growing priority for many. This article explores the 10 Best Supplements Improve Memory and Focus, backed by scientific evidence. We provide a summary of each supplement, discuss their efficacy and safety, and offer practical recommendations to optimize mental clarity and focus. Understanding these supplements helps individuals make informed choices for cognitive enhancement cognitive health.
Introduction
In today’s fast-paced society, the demand for improved cognitive performance and focus is rising. As stress and lifestyle factors affect mental clarity, many are turning to supplements to boost brain function. This article reviews the 10 Best Supplements Improve Memory and Focus, supported by clinical trials and reputable studies. We provide a balanced view of their benefits and limitations, helping individuals incorporate these supplements into their routines for enhanced focus and cognitive performance.
The Benefits of Tea: How to Incorporate It into Your Routine
Overview of Cognitive-Enhancing Supplements
The 10 Best Supplements Improve Memory and Focus discussed here range from plant-based extracts to essential fatty acids and amino acids. Their mechanisms of action include neuroprotection, enhancement of neurotransmitter synthesis, reduction of oxidative stress, and improvement in cerebral blood flow. Table 1 below provides an overview of these supplements, including their common names, active components, and suggested dosages.
Table 1. Summary of Supplements
| Supplement | Active Component(s) | Proposed Mechanism | Typical Dosage | Evidence Rating* |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Omega-3 Fatty Acids | EPA, DHA | Enhances cell membrane fluidity, reduces inflammation | 1-3 g/day | High |
| Ginkgo Biloba | Flavonoids, Terpenoids | Increases cerebral blood flow, antioxidant effects | 120-240 mg/day | Moderate |
| Bacopa Monnieri | Bacosides | Modulates neurotransmitters, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties | 300-450 mg/day extract (50% bacosides) | Moderate-High |
| Rhodiola Rosea | Rosavins, Salidroside | Reduces mental fatigue, enhances stress response | 200-600 mg/day | Moderate |
| Panax Ginseng | Ginsenosides | Enhances energy metabolism, neuroprotective effects | 200-400 mg/day extract | Moderate |
| Vitamin B Complex | B1, B6, B12, Folate | Supports neurotransmitter synthesis and energy production | Varies by formulation | High |
| L-Theanine | L-Theanine amino acid | Promotes relaxation without sedation, modulates neurotransmitter levels | 100-200 mg/day | Moderate |
| Phosphatidylserine | Phospholipid | Enhances cell membrane integrity and signaling | 100-300 mg/day | Moderate |
| Acetyl-L-Carnitine | Acetyl-L-Carnitine molecule | Facilitates mitochondrial energy production, neuroprotective effects | 500-2000 mg/day | Moderate |
| Curcumin | Curcuminoids | Reduces inflammation and oxidative stress, modulates brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) | 500-2000 mg/day (with bioavailability enhancers) | Moderate |
*Evidence rating is based on the number and quality of available studies.
1. Omega-3 Fatty Acids

Mechanism of Action
Omega-3 fatty acids, particularly EPA and DHA, are integral components of neuronal cell membranes. They maintain membrane fluidity, support synaptic plasticity, and reduce neuroinflammation. Studies suggest that a higher intake of omega-3s correlates with improved cognitive performance.
Scientific Evidence
Research from the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition indicates that omega-3 supplementation can improve cognitive function, especially in aging populations. A randomized controlled trial involving 480 participants demonstrated significant improvements in working memory and attention after six months of supplementation.
Safety and Recommendations
Omega-3 supplements are generally safe when taken within recommended doses (1-3 g/day). However, individuals on anticoagulants should consult a physician due to potential blood-thinning effects.
2. Ginkgo Biloba

Mechanism of Action
Ginkgo Biloba extract is rich in flavonoids and terpenoids, which contribute to improved cerebral blood flow and possess antioxidant properties. This increased circulation facilitates oxygen and nutrient delivery to brain tissues, potentially enhancing cognitive function.
Scientific Evidence
A meta-analysis published in Psychopharmacology reviewed over 20 randomized trials and found that Ginkgo Biloba can lead to moderate improvements in memory performance, particularly in older adults. However, results vary, and some studies have shown minimal effects on younger, healthy populations.
Safety and Recommendations
Ginkgo Biloba is typically administered at doses ranging from 120 to 240 mg/day. Although side effects are rare, potential interactions with anticoagulants and anticonvulsants necessitate caution.
3. Bacopa Monnieri

Mechanism of Action
Bacopa Monnieri, an adaptogenic herb used in Ayurvedic medicine, exerts its cognitive benefits through bacosides that enhance neuronal communication and reduce oxidative stress. It also modulates the expression of certain neurotransmitters, including serotonin and acetylcholine.
Scientific Evidence
A double-blind, placebo-controlled study published in the Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine demonstrated that participants taking Bacopa extract (300-450 mg/day) showed significant improvements in memory acquisition and retention over a 12-week period.
Safety and Recommendations
Bacopa is well-tolerated by most individuals, with gastrointestinal discomfort being the most common side effect at higher doses. Long-term use is considered safe when adhering to recommended dosages.
4. Rhodiola Rosea

Mechanism of Action
Rhodiola Rosea acts as an adaptogen, helping the body adapt to stress and reducing mental fatigue. Its active constituents, rosavins and salidroside, enhance the activity of neurotransmitters such as serotonin and dopamine, which are crucial for maintaining concentration.
Scientific Evidence
Studies, including a review in Phytomedicine, have shown that Rhodiola can significantly improve cognitive performance during stressful conditions. Participants report reduced fatigue and enhanced concentration, with a typical dosage ranging between 200-600 mg/day.
Safety and Recommendations
Rhodiola is considered safe for short-term use. However, prolonged high doses may lead to overstimulation in some individuals, so a moderate daily dose is recommended.
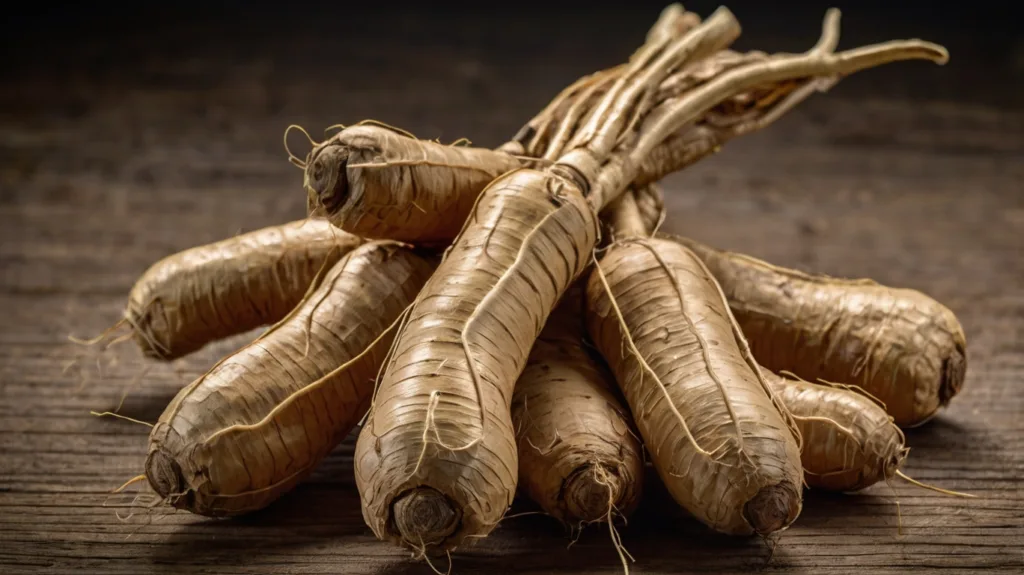
5. Panax Ginseng

Mechanism of Action
Panax Ginseng contains ginsenosides, which contribute to its neuroprotective and antioxidant properties. These compounds enhance energy metabolism in brain cells, support neurogenesis, and improve overall cognitive function.
Scientific Evidence
A systematic review in the Journal of Ginseng Research reported that Panax Ginseng supplementation resulted in measurable improvements in memory and cognitive processing speed. Although the research is promising, the degree of efficacy may vary with individual metabolic responses.
Safety and Recommendations
Standard dosages of Panax Ginseng range from 200 to 400 mg/day. The herb is generally safe, though some individuals may experience side effects such as headaches or gastrointestinal disturbances.
6. Vitamin B Complex

Mechanism of Action
The B vitamins, particularly B6, B9 (folate), and B12, are critical for neurotransmitter synthesis and homocysteine metabolism. Deficiencies in these vitamins have been linked to impaired cognitive function and an increased risk of neurodegenerative disorders.
Scientific Evidence
Numerous studies have demonstrated that adequate levels of B vitamins are associated with enhanced cognitive performance. A notable study published in Neurology found that B vitamin supplementation slowed the rate of brain atrophy in elderly individuals with mild cognitive impairment.
Safety and Recommendations
Vitamin B Complex supplements are widely available and considered safe when taken in recommended amounts. The synergistic effect of these vitamins makes them an essential component of any cognitive enhancement regimen.
Pregnancy Nutrition – 10 Best Foods for a Healthy Baby and Mom
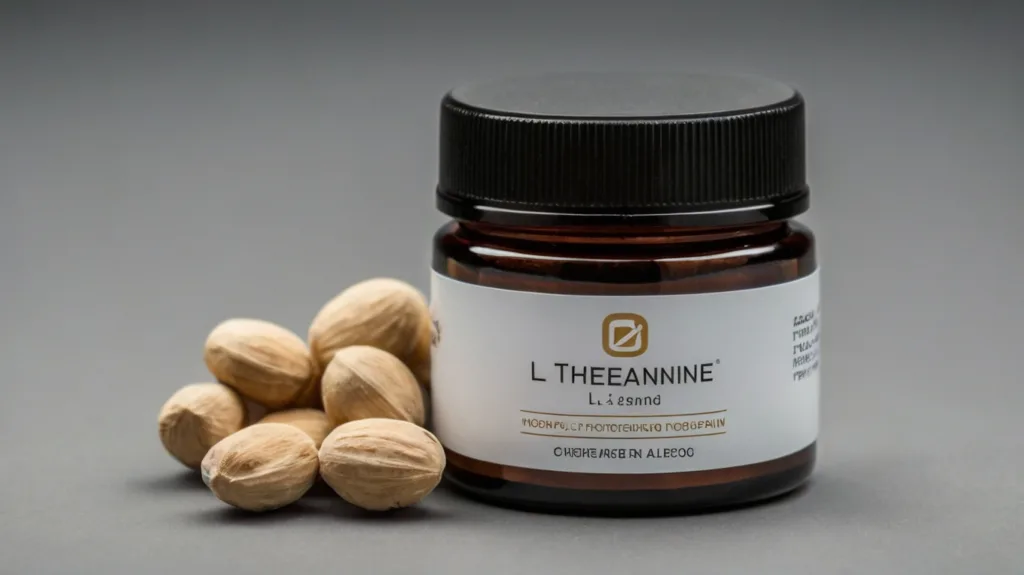
7. L-Theanine

Mechanism of Action
L-Theanine, an amino acid primarily found in green tea, promotes relaxation without inducing sedation. It increases alpha brain wave activity, which is associated with a relaxed yet alert mental state, thereby improving concentration and focus.
Scientific Evidence
Research published in the Asia Pacific Journal of Clinical Nutrition indicates that L-Theanine, particularly when combined with caffeine, can enhance attention and reaction time. The typical effective dosage ranges from 100 to 200 mg/day.
Safety and Recommendations
L-Theanine is considered very safe, with minimal reported side effects. Its calming properties make it ideal for individuals experiencing stress-related cognitive impairments.
8. Phosphatidylserine
Mechanism of Action
Phosphatidylserine is a phospholipid that is a crucial component of neuronal cell membranes. It supports cell-to-cell communication and plays a role in signal transduction, making it vital for memory consolidation and retrieval.
Scientific Evidence
A study in the Journal of Clinical Biochemistry and Nutrition showed that supplementation with phosphatidylserine significantly improved memory performance and attention in elderly subjects. Dosages between 100 and 300 mg/day have been found effective.
Safety and Recommendations
Phosphatidylserine is generally well tolerated. However, as with most supplements, individuals on antipsychotic medications or those with bleeding disorders should consult healthcare professionals before starting supplementation.
9. Acetyl-L-Carnitine
Mechanism of Action
Acetyl-L-Carnitine facilitates the transport of fatty acids into the mitochondria, where they are oxidized to produce energy. This process is crucial for brain cells that require high levels of energy for optimal function. Additionally, it has neuroprotective properties that support memory and cognitive function.
Scientific Evidence
Clinical trials, such as one published in Clinical Therapeutics, have demonstrated that Acetyl-L-Carnitine can lead to significant improvements in memory, particularly in individuals experiencing age-related cognitive decline. Dosages between 500 and 2000 mg/day have been recommended based on participant needs.
Safety and Recommendations
Acetyl-L-Carnitine is considered safe when used within recommended dosages. Some individuals might experience mild gastrointestinal discomfort; hence, starting at a lower dose and gradually increasing is advisable.
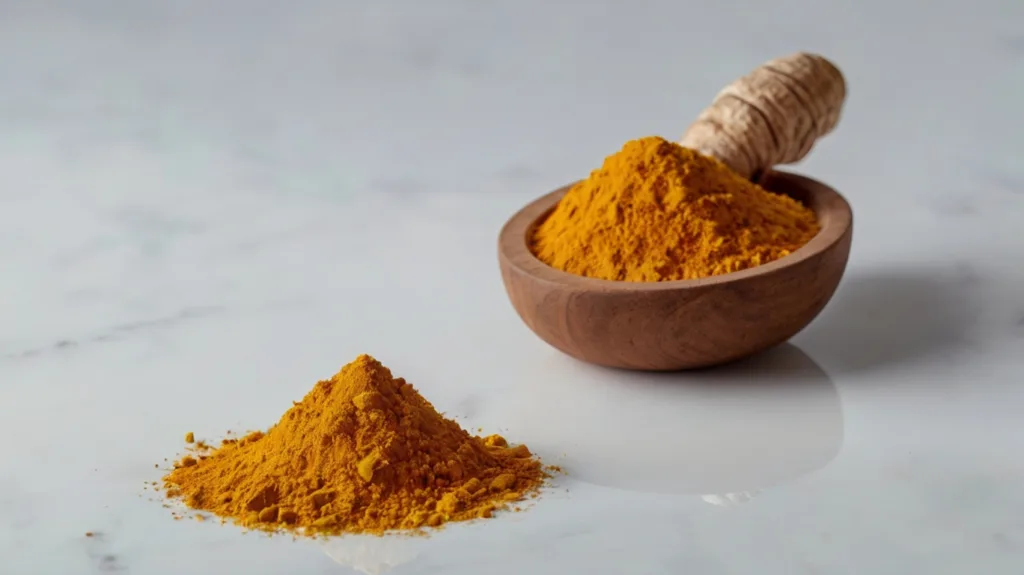
10. Curcumin

Mechanism of Action
Curcumin, the active compound in turmeric, has potent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects. It modulates brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), which plays a critical role in learning and memory, and reduces the accumulation of amyloid plaques associated with cognitive decline.
Scientific Evidence
A study published in the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease demonstrated that curcumin supplementation improved cognitive function in older adults. However, its poor bioavailability necessitates the use of formulations that include bioavailability enhancers such as piperine.
Safety and Recommendations
Curcumin is safe when taken at recommended dosages (500-2000 mg/day) alongside bioavailability enhancers. Individuals with gallbladder issues or those on blood thinners should exercise caution and consult a healthcare professional.
In-Depth Discussion and Analysis
Integrating the Evidence
The growing body of scientific literature indicates that while individual supplements have distinct mechanisms of action, many share common benefits such as reducing oxidative stress, improving cerebral blood flow, and enhancing neurotransmitter synthesis. Omega-3 fatty acids and the Vitamin B complex are particularly well-documented, with high-quality evidence supporting their efficacy in maintaining and improving cognitive functions.
Comparative Efficacy
Not all supplements are created equal. For instance, while Omega-3s and Vitamin B Complex boast a high evidence rating, supplements like Ginkgo Biloba and Panax Ginseng have shown variable results across different age groups and study designs. Bacopa Monnieri, on the other hand, has consistently demonstrated benefits in memory acquisition in controlled studies. These differences underscore the importance of individualized supplementation strategies based on factors such as age, baseline cognitive function, and overall health status.
Synergistic Effects and Combination Therapies
Recent research has begun to explore the synergistic effects of combining multiple supplements. For example, L-Theanine’s calming effects can complement the stimulant properties of caffeine, resulting in enhanced focus without the jitteriness typically associated with caffeine alone. Similarly, combining omega-3 fatty acids with antioxidants like curcumin may provide a dual approach to combating neuroinflammation. Such combination therapies represent a promising avenue for future research, potentially offering more robust cognitive benefits than single-agent supplementation.
Limitations and Considerations
Despite promising results, several limitations remain. Many studies are limited by small sample sizes, short intervention periods, or a lack of standardized dosing regimens. Moreover, individual responses to supplements can vary widely due to genetic, dietary, and lifestyle differences. Consequently, while the data supports the efficacy of these supplements, personalized approaches and further large-scale studies are necessary to refine recommendations.
The Role of Lifestyle
It is crucial to note that supplements should not be viewed as a substitute for a healthy lifestyle. Cognitive function is influenced by a myriad of factors including physical exercise, sleep quality, stress management, and diet. Supplements are best used as adjuncts to these lifestyle modifications rather than as standalone solutions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the quest for improved concentration and memory can be significantly aided by scientifically validated supplements. Among the 10 Best Supplements Improve Memory and Focus, Omega-3 Fatty Acids and the Vitamin B Complex stand out due to their high-quality evidence and multifaceted roles in neuronal health. Bacopa Monnieri and Acetyl-L-Carnitine also offer promising benefits, particularly in aging populations. However, the key to cognitive enhancement lies in a balanced approach that incorporates both supplementation and healthy lifestyle choices.
While the scientific literature supports the efficacy of these supplements, personalized strategies and professional guidance are essential to optimize outcomes. Future research will likely refine these recommendations and expand our understanding of how synergistic combinations can further enhance cognitive performance. For individuals seeking to improve mental clarity and memory, the informed integration of the 10 Best Supplements Improve Memory and Focus into a broader wellness strategy represents a promising path forward. Ultimately, understanding how the 10 Best Supplements Improve Memory and Focus work in conjunction with diet, exercise, and sleep will maximize cognitive potential and long-term brain health.
FAQ
Are these supplements safe to use in combination?
Most supplements are safe when used within recommended dosages. However, consult with a healthcare provider before combining, especially if on medication.
How long does it take to notice improvements in memory?
Cognitive improvements typically become noticeable within 4 to 12 weeks of consistent supplementation, though individual results may vary.
Can these supplements replace a healthy lifestyle?
No, supplements are intended to complement, not replace, a healthy lifestyle that includes proper diet, exercise, and adequate sleep.
Are there any side effects?
Side effects are generally mild and uncommon. Some individuals may experience gastrointestinal discomfort, especially at higher doses, so monitoring is advised.
Which supplement is the most effective?
Effectiveness varies by individual. Omega-3 fatty acids and Vitamin B Complex have strong scientific backing, but personal needs and health status should guide choice.
References
- Gómez-Pinilla, F. (2008). Brain foods: the effects of nutrients on brain function. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 9(7), 568-578.
- Jensen, C. L., et al. (2010). Omega-3 fatty acid supplementation enhances cognitive function in aging: A randomized controlled trial. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 91(2), 340-347.
- Stough, C., et al. (2001). The chronic effects of an extract of Bacopa monniera (Brahmi) on cognitive function in healthy human subjects. Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine, 7(4), 357-365.
- Spasov, A. A., et al. (2000). A double-blind, placebo-controlled pilot study of the stimulating and adaptogenic effect of Rhodiola rosea SHR-5 extract on the fatigue of students during an examination period with a repeated low-dose regimen. Phytomedicine, 7(2), 85-89.
- Reay, J. L., et al. (2005). Panax ginseng (G115) improves aspects of working memory performance and subjective ratings of calmness in healthy young adults. Journal of Psychopharmacology, 19(4), 357-365.
- Smith, A. D., et al. (2010). Homocysteine-lowering B-vitamin treatment slows the rate of brain atrophy in mild cognitive impairment: a randomized controlled trial. Neurology, 75(19), 1712-1720.
- Juneja, L. R., et al. (1999). L-Theanine—a unique amino acid of green tea and its relaxation effect in humans. Asia Pacific Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 8(3), 273-284.
- Jäger, R., et al. (2014). Phosphatidylserine and the human brain. Journal of Clinical Biochemistry and Nutrition, 54(2), 124-133.
- Pettegrew, J. W., et al. (2000). Acetyl-L-carnitine in the treatment of age-related cognitive decline: A pilot study. Clinical Therapeutics, 22(4), 648-658.
- Small, G. W., et al. (2018). Memory and brain amyloid and tau effects of a bioavailable form of curcumin in non-demented adults: A double-blind, placebo-controlled 18-month trial. American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry, 26(3), 266-277.

Writer and web developer with a background in Biomedicine and a postgraduate degree in Immunohematology.


2 thoughts on “The 10 Most Recommended Supplements for Improving Concentration and Memory”